What is Physics?The study of matter, its characteristics, such as its motion and behavior across space and time, as well as the associated amounts of energy and force, is covered in the scientific field of physics. One of the earliest fields of science is physics. With each new discovery in the actual world, we learn something new. As hypotheses are created and advancements are achieved over time, both the query and the solution alter.
The underlying rules of the universe are understood and described using the study of physics. Starting from tiny particles that constitute matter to the massive forces that rule the cosmos, physics comprises of many topics and concepts. The word physics is made from the Greek word physikos meaning natural or physical.
New technologies are frequently made possible by improvements in physics. For example let us consider, our knowledge of physics and its subfields have led us to create goods such as television, computers, home appliances, and nuclear weapons. Similarly, improvements in thermodynamics have drastically affected the growth of industrialization, and improvements in mechanics have influenced the creation of calculus.
 Branches of Physics
Branches of Physics
Various concepts are studied in the field of Physics. Physics is divided into categories based on the topics studied in those subfields.
- Mechanics
- Optics
- Thermodynamics
- Electromagnetism
- Atomic and Nuclear Physics
Mechanics Mechanics study how matter, force, and motion are related to one another with respect to physical objects. The three branches of mechanics are :
- Statics, which studies forces acting on and inside a body when it is at rest,
- Kinematics, which defines possible motions of a body or system of bodies,
- Kinetics, which explains or predicts the motion that will occur in a certain situation or specific condition.
 Optics
Optics The behavior and qualities of light, particularly how it interacts with materials and how to create devices that can either use or detect it, are the focus of the branch of physics known as optics. Visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light behavior is often described by the science of optics. Light has many properties in common with X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves because it is an electromagnetic wave.
 Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics The study of the interaction between heat, work, temperature, and energy is known as thermodynamics. Thermodynamics broadly refers to the process of moving energy from one location or form to another. The fundamental principle is that heat is a kind of energy that is equivalent to a specific quantity of mechanical labour.
 Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism The study of charge and the fields and forces it generates is known as electromagnetism. Two components of electromagnetism are electricity and magnetism. One of the four basic forces of nature is the electromagnetic force. In interactions between atoms and molecules, it is the dominating force. Electromagnetism can be referred to as a mixture of electrostatics and magnetism, two separate interrelated phenomena. Magnetism is an interaction that only happens between charged particles in relative motion, whereas electromagnetic forces happen between any two charged particles, generating an attraction between particles with opposing charges and repulsion between particles with the same charge.
 Atomic and Nuclear Physics
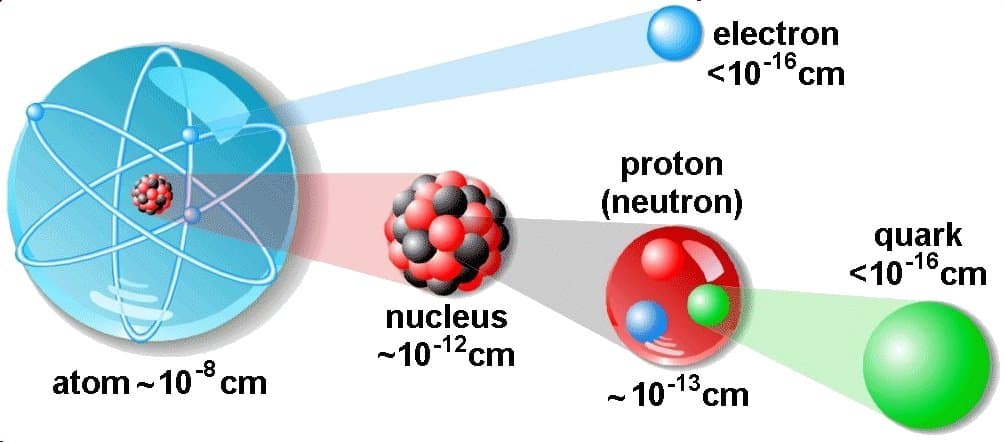
Atomic and Nuclear Physics The atomic nucleus’ structure and the radiation that results from unstable nuclei are the subjects of this branch of physics. In addition to researching other types of nuclear matter, the study of atomic nuclei, their components, and their interactions is known as nuclear physics. Atomic physics, which examines the atom as its whole, including its electrons, should not be confused with nuclear physics.