Accounts payable (AP) tracks money owed to creditors. Examples include bank loans, unpaid bills and invoices, debts to suppliers or vendors, and credit card or line of credit debts. Rarely, the term "trade payables" is used in place of "accounts payable." Accounts payable belong to a larger class of accounting entries known as liabilities.
Assets
Assets are items of value, or resources that a business owns or controls. More technical and precise definitions specify two technicalities: First, assets result from past business activities. Second, they will or are expected to generate future economic value. Assets come in many types and classes. Types include current and noncurrent, operating and nonoperating, physical, and intangible. Classes include broad categories such as cash and equivalents, equities, commodities, real estate, intellectual property, and fixed income, among others.
Capital
In common usage, capital (abbreviated "CAP.") refers to any asset or resource a business can use to generate revenue. A second definition considers capital the level of owner investment in the business. The latter sense of the term adjusts these investments for any gains or losses the owner(s) have already realized.Accountants recognize various subcategories of capital. Working capital defines the sum that remains after subtracting current liabilities from current assets. Equity capital specifies the money paid into a business by investors in exchange for stock in the company. Debt capital covers money obtained through credit instruments such as loans.
Types Of Accounting
If you studied business, you know that accounting is more than staring at balance sheets all day. There are many different types of accounting that require different skill sets. Your business may need to work with a certain specialty based on their needs. Below, we’ll discuss some common forms of accounting you might encounter.
Tax Accounting
Tax accounting involves maintaining and keeping track of your business’ taxes. This can include filing yearly taxes, tracking spending and tax rates, as well as assisting employees with setting up tax
Financial Accounting
To do this type of accounting, you’ll have to have a solid understanding of how to file taxes and of your tax code. You’ll need to comply with both federal regulations and the states in which you operate your business.
Management Accounting
Management accountants present financial data to stakeholders and senior leadership at a company. They play a greater role in reviewing what products or services a company needs, as well as how these efforts can be financed.
Cost Accounting
Cost accountants create a constant record of all costs incurred by the business. This data is used to track where the company spends and improve the management of these expenses. They can find redundancies and places where the company could cut costs.
.webp) Accounting Skills
Accounting Skills
Being a rockstar accountant is more than just being good with numbers. You need a vast array of knowledge on tax codes, financial regulations, and the best practices for maintaining a healthy balance sheet. Then, you need the soft skills to apply your knowledge to the real world. Here are some essential skills accounting requires.
Listening
If you’re on the prowl for an accountant, you want to find one that listens. They should understand what your business does, the expenses required for you to operate, and any financial challenges you might have on your radar.
If you are the accountant providing services, you’ll need to provide a listening ear. You can better apply your knowledge if you have a clear understanding of a client’s needs.
Time Management
Whether you're using in-house accounting services or working with external accountants, time management is an essential skill. Your team is faced with internal deadlines and audits. Reviews of your financial health need to be completed in a timely way.
If you’re an accountant, remember many of your clients will have the same deadlines. Tax day and the financial year are big markers for the organizations you work with. Make sure you can manage your book of business so no one’s needs fall through the cracks.
Organization
As an accountant, you need to be able to offer timely suggestions and recommendations to your clients. So, you’ll need to be organized. Keep track of where information is for all of your different clients. That should include secure storage systems for all of their documents.
As an accountant, you're dealing with sensitive information. You should have safe channels for transferring these documents so the data is safe from bad actors.
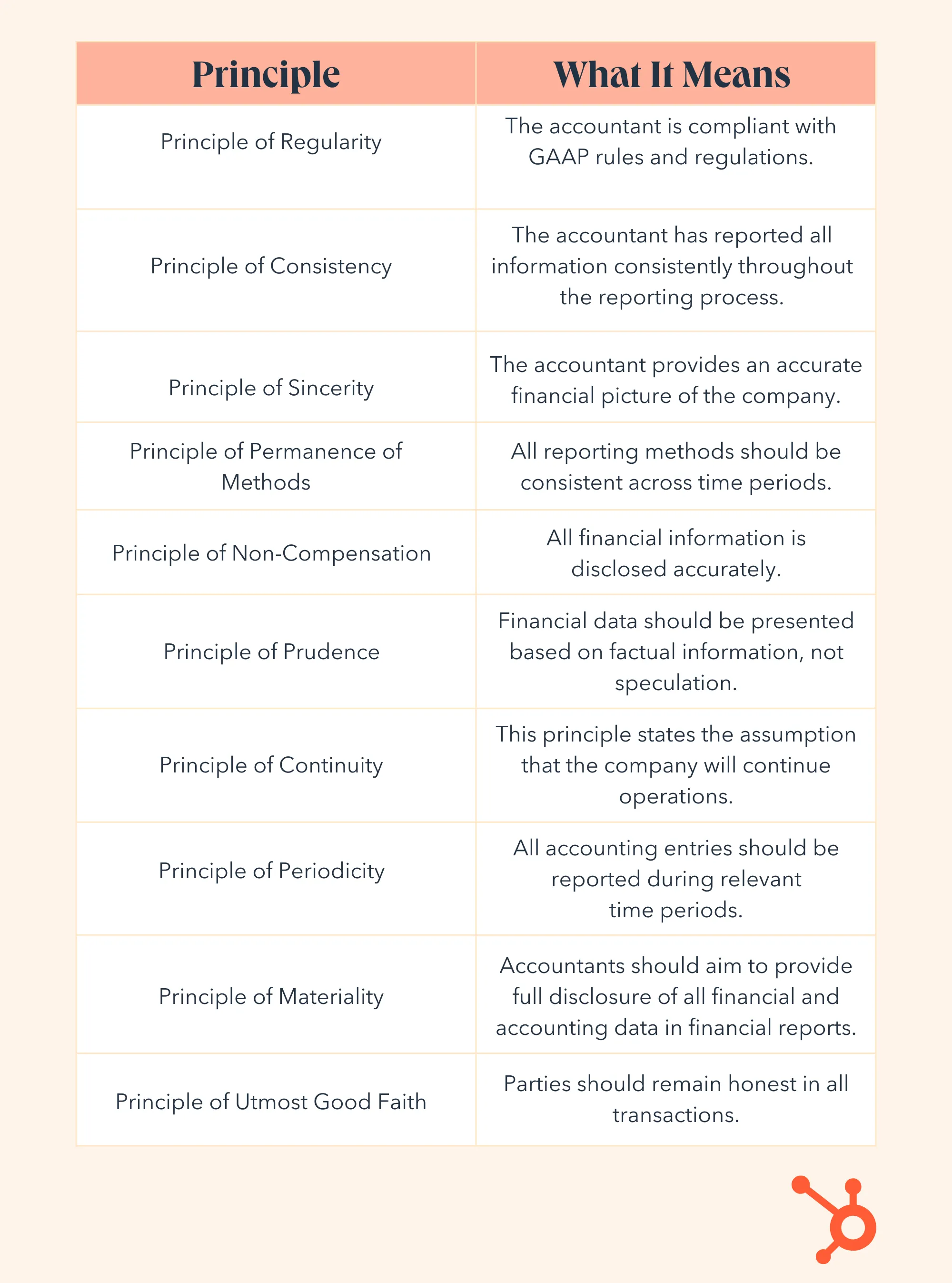
Accounting principles
The Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) are a blueprint for accounting across sectors in the U.S. These principles confirm that publicly traded companies share their finances accurately.
By law, accountants for all publicly traded companies must comply with GAAP. Let’s break down these principles.


.webp) Accounting Skills
Being a rockstar accountant is more than just being good with numbers. You need a vast array of knowledge on tax codes, financial regulations, and the best practices for maintaining a healthy balance sheet. Then, you need the soft skills to apply your knowledge to the real world. Here are some essential skills accounting requires.
Accounting Skills
Being a rockstar accountant is more than just being good with numbers. You need a vast array of knowledge on tax codes, financial regulations, and the best practices for maintaining a healthy balance sheet. Then, you need the soft skills to apply your knowledge to the real world. Here are some essential skills accounting requires. 